Thanks to their modular design, the DSC instruments as part of the METTLER TOLEDO Thermal Analysis Premium or Excellence Line are the best choice for manual or automatic operation, from academic research and industrial development to quality assurance and production.
Measure samples with the most sensitive DSC on the market – ideal for investigating all kinds of materials and effects
The DSC utilizes an innovative patented DSC sensor with 120 thermocouples which guarantees unmatched sensitivity.

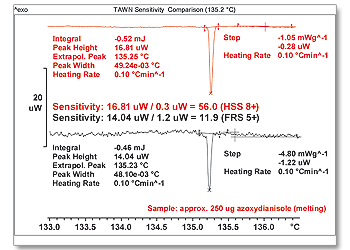
Amazing sensitivity
A quantum jump in sensor technology enables us to offer the highest sensitivity sensors available in DSC instrumentation and allows you to detect the weakest thermal effects. The signal-to-noise ratio, an important instrument parameter, is determined by the number of thermocouples and their specific arrangement.

Outstanding resolution
The signal time constant determines how well close-lying or overlapping thermal effects are separated from one another. We set unprecedented and unparalleled performance standards due to our high thermal conductivity ceramic sensor material with its low thermal mass.

Modular concept
Face your new measurement requirements with flexibility: protect your investment through the modularity and upgradeability of our innovative instrument solutions.
Thermal Analysis Knowledge – Quarterly News on Applications, Webinars, Courses and How-to-Videos
Documentation
Brochures
Datasheets
Services
Explore Our Services - Tailored to Fit Your Equipment
According to the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC), thermal analysis is group of techniques in which a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature while the substance is subjected to a controlled temperature program.
Training & Consulting

Applications
New Applications, Review of Analytical Topics, Practical Tips
Thermal Analysis Applications
Advanced Search Overview
The future of thermal analysis
Hundreds of interesting articles on thermal analysis are now available from METTLER TOLEDO. They describe new applications, review analytical topics or give practical tips on how to perform and evaluate measurements. The articles have been taken from UserCom, our bi-annual technical customer journal, and from our comprehensive application handbooks.
Take advantage of METTLER TOLEDO’s more than 40 years of experience in thermal analysis











