Compositional Analysis Instruments
Thermogravimetric Analysis for Complex Analysis
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is a thermal analysis technique used to study the compositional analysis of materials by measuring the mass change of a sample as a function of temperature or time. TGA can be used to determine the thermal stability of a sample, identify the decomposition temperature, and analyze the composition of complex materials.
Advantages
Modular Design
Modularity is at the core of METTLER TOLEDO thermal analyzers enabling us to offer tailor-made solutions for almost all academic and industrial applications. Should requirements change after installation, the instrument can be upgraded as needed.
Reliable Automation
Our TGA and DSC systems support fully automated workflows – from sample loading to result analysis and report generation. Up to 34 samples can be processed by our robust, factory endurance-tested sample robot.
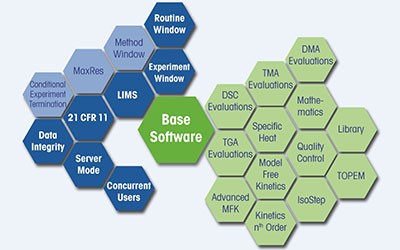
One Software for All Thermal Analysis Instruments
STARe is the most complete and comprehensive thermal analysis software, providing unrivalled flexibility, unlimited evaluation possibilities and the technical controls to support compliance.

Innovative Sensor Technology
Put your trust in METTLER TOLEDO’s world-leading sensor technology: Whether you purchase a DSC, TGA, TMA or DMA instrument, we guarantee exceptional sensitivity and highly accurate measurement results.
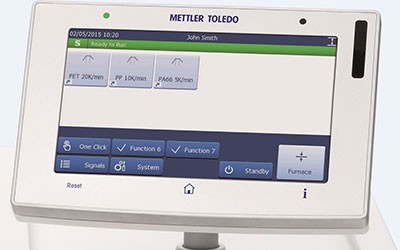
Simple Operation
STARe functionality is readily accessible from the software's intuitive ribbon interface. Standard features such as OneClick™ and multiple curve handling, as well as options like Quality Control and Reference Library, simplify daily lab work.

High-Level Competence & Support
Our global network of application specialists gives you access to the latest application know-how. Dedicated application specialists help to ensure that you obtain the most accurate thermal analysis results.
Explore Our Services - Tailored to Fit Your Equipment
According to the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC), thermal analysis is group of techniques in which a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature while the substance is subjected to a controlled temperature program.
Support & Repair

Training & Consulting

FAQs
What types of samples can be analyzed with thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) for compositional analysis?
TGA can be used to analyze a wide range of materials, including polymers, composites, minerals, pharmaceuticals, and food products, among others. Any material that undergoes thermal decomposition or reaction can be studied with TGA.
What information can be obtained from thermogravimetric analysis in terms of compositional analysis?
TGA can provide information about the amount and type of materials present in a sample, as well as their thermal stability, decomposition profile, and reaction kinetics. It can also be used to identify the presence of impurities or contaminants in a material.
How does TGA compare to other thermal analysis techniques for compositional analysis?
TGA is a versatile and widely used technique for compositional analysis, but it is not the only thermal analysis technique available. Other techniques, such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermomechanical analysis (TMA), can provide complementary information about a sample's thermal behavior and mechanical properties.
Can thermogravimetric analysis be used for quantitative compositional analysis?
Yes, TGA can be used for quantitative compositional analysis by measuring the mass loss of a sample as a function of temperature and comparing it to a reference sample or calibration curve. This method can be used to determine the amount of each component present in a mixture or composite material.
Are there any limitations or challenges to thermogravimetric analysis for compositional analysis?
One limitation of TGA is that it cannot provide information about the specific chemical bonds or functional groups present in a sample. Additionally, the thermal stability and behavior of a sample can be affected by factors such as sample preparation, heating rate, and atmosphere, which can make interpretation of the data more challenging.