Heat Capacity Determination Instruments
Investigate the Cp of your Materials with Thermal Analysis
Heat capacity (Cp) is a physical property that describes the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance. The Cp of a material can have important implications for many physical and chemical processes, including material processing, energy storage, and heat transfer.
Advantages
Modular Design
Modularity is at the core of METTLER TOLEDO thermal analyzers, enabling us to offer tailor-made solutions for almost all academic and industrial applications. Should requirements change after installation, the instrument can be upgraded as needed.
Reliable Automation
Our TGA and DSC systems support fully automated workflows – from sample loading to result analysis and report generation. Up to 34 samples can be processed by our robust, factory endurance-tested sample robot.
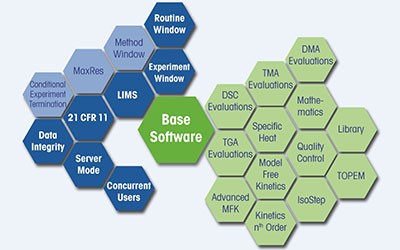
One Software for All Thermal Analysis Instruments
STARe is the most complete and comprehensive thermal analysis software, providing unrivalled flexibility, unlimited evaluation possibilities and the technical controls to support compliance.

Innovative Sensor Technology
Put your trust in METTLER TOLEDO’s world-leading sensor technology: whether you purchase a DSC, TGA, TMA, or DMA instrument, we guarantee exceptional sensitivity and highly accurate measurement results.
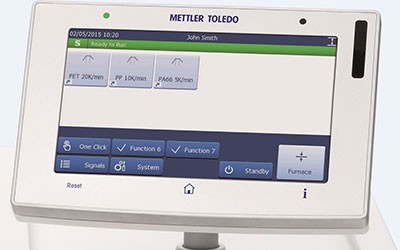
Simple Operation
STARe functionality is readily accessible from the software's intuitive ribbon interface. Standard features, such as OneClick™ and multiple curve handling, as well as options like Quality Control and Reference Library, simplify daily lab work.

High-Level Competence & Support
Our global network of application specialists gives you access to the latest application know-how. Dedicated application specialists help to ensure that you obtain the most accurate thermal analysis results.
Explore Our Services - Tailored to Fit Your Equipment
According to the International Confederation for Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (ICTAC), thermal analysis is group of techniques in which a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature while the substance is subjected to a controlled temperature program.
Support & Repair

Training & Consulting

FAQs
What types of instruments are used to measure the heat capacity of materials?
The heat capacity of materials is usually measured by a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). In certain cases, especially at higher temperatures, a thermogravimeter (TGA/DSC) can be used.
What is the difference between heat capacity and specific heat capacity?
Heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a substance by a certain amount, usually one degree Celsius or Kelvin. Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit of mass (such as one gram) of a substance by a certain amount, usually one degree Celsius or Kelvin.
How does differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measure the specific heat capacity of materials?
In the STARe software, six different methods are available to determine specific heat capacity of a material. They can separate out the sensible heat capacity (reversing heat flow) and the latent heat capacity (non-reversing heat flow) of a material.
What is the difference between the sensible heat capacity and latent heat capacity of a material?
Sensible heat capacity and latent heat capacity are two related but distinct physical properties that describe a material's ability to store thermal energy. Sensible heat capacity refers to the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a material without changing its state or phase. Latent heat capacity, on the other hand, refers to the amount of heat energy required to change the state or phase of a material without changing its temperature.