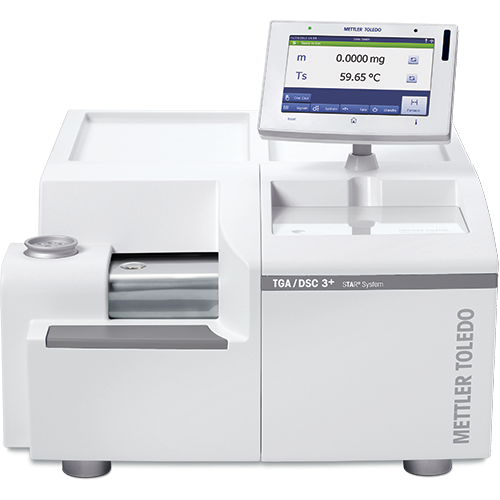
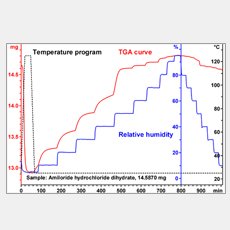
TGA/DSC, or Thermal Gravimetric Analysis/Differential Scanning Calorimetry, is an important technique used in material characterization. It is commonly used in research and extensively in the polymer, chemical, battery, renewable energy, pharmaceutical, and food industries. A TGA/DSC instrument operates over a large temperature range, typically from room temperature to 1600 °C.
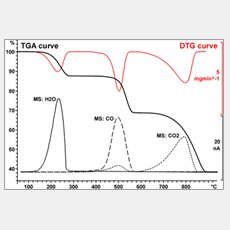
TGA results provide information about the change in weight of a sample as it is heated, which is useful for determining material composition, purity, decomposition, and thermal stability. DSC provides information about the heat flow (energy) into or out of a sample as it is heated, cooled, or held at a constant temperature, which is useful for studying thermal events such as the glass transition, phase changes, and chemical reactions. These techniques can be combined into a single TGA/DSC analyzer to study a variety of materials, including polymers, composites, battery components, chemicals, metals, foods, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals. It is particularly useful in the fields of new material development, failure analysis, and quality control.
The information obtained from TGA/DSC analysis can therefore be used to optimize manufacturing processes, improve product performance, and ensure regulatory compliance. It can also help to identify potential safety concerns, such as the presence of hazardous materials or unexpected reactions.
Overall, TGA/DSC analysis is a powerful technique that provides detailed information about a wide range of material properties, helping to improve quality and safety. This can aid identification, material selection, design, and optimization across many industries, as well as facilitate academic and industrial research.